Table of Contents
- General
- Illuminances (Lighting Levels)
- Lampfittings
- Special Design Requirements
- Supply System
- Lighting Panels
- Convenience Outlets and Handlamps
- Emergency Lighting
- Coding System of Lampfittings
- Appendix I “Lighting Intensities”
Lighting installation and materials installed in plants shall be suitable for the hazard classification and corrosive atmosphere of the area concerned.
The wiring shall be always in cable for outdoor areas and for indoor areas in cable (preferable) or in PVC conduit, depending on the architect’s decision.
Underground cables shall be laid as indicated in standard BN-DS-E3.
Overhead cables shall be installed as per standard BN-DS-E7, part 1 and part 3.
Lampfittings, convenience outlets and switches shall be installed as per standard BN-DS-E7, part 3.
2. Illuminances (Lighting Levels)
Lighting installations shall be designed to provide minimum average illuminances not less than those recommended by Client. Failing Client’s requirements Company’s recommended illuminances as tabulated in appendix 1 to this design standard shall be used.
Supplemental lighting required for bench work, close detailed work, frequent operation, presence of control valves or instruments, etc. shall be reviewed on an individual basis.
The uniformity ratio of illuminances (Emin/Emax) to be provided for the various areas shall be limited as listed below:
- Outdoor operating area 1 : 2,5
- Outdoor non-operating area 1 : 5
- Road lighting 1 : 10
- Indoor areas, continuously occupied or where difficult visual tasks are performed 1 : 1,5
In general, indoor and outdoor areas shall be illuminated with fluorescent type lampfittings with single pin, instant start type tubes for classified areas and bi-pin, switch start type tubes for non-classified building lighting.
The lamp colours shall be “white” colour 4200 K.
High pressure gas discharge lamps should be considered for road or perimeter lighting, open areas and areas where a high illuminance is required.
Transparant gauge glasses will normally be illuminated with back-mounted fluorescent type lampfittings.
Lampfittings for air-craft warning will consist of a double lamp unit with built-in automatic switch to the standby lamp upon failure of the one in service. (e.g. Philips type 17140).
Generally, lampfittings within reach, or where exposed to breakage shall be equipped with metal guards.
All fluorescent and high pressure gas discharge lampfittings shall be provided with individual power factor correction capacitors.
4. Special Design Requirements
Location of floodlights at sufficiently elevated platforms on process equipment shall be considered rather than using separate poles or towers.
The need for plant road lighting shall be reviewed in conjunction with the possible spill lighting from the plant lighting installation.
If required, street lighting lampfittings shall be individually protected and/or switched by means of circuit breakers housed in a box mounted in the pole.
Air craft warning lights (if required) shall be installed in accordance with the requirements of chapter 6 of Annex 14 to the Convention on International Civil Aviation.
They shall have safe access for maintenance and relamping by means of permanent ladders and platforms or by a suitable method for raising and lowering the fittings.
Lighting for control rooms requires that emphasis be placed on vertical plane illumination without shadows and reflections.
This shall be achieved by the use of either a diffuse or a directional lighting system:
-
Diffuse lighting system
This system will normally be made with a ceiling consisting of an open network of translucent vanes through which the light passes from normal fluorescent lampfittings mounted in the cavity above.
The ratio of spacing of the lampfittings to the distance from top of louvers to bottom of lampfittings should be not over 1,5 to 1 to obtain an equal illuminance.
(It is noted that a lot of pipes and ducts for other services will also run in this cavity, which requires a good coordination for location of lampfittings). -
Directional lighting system
For this system normally a false ceiling will be provided with flush mounted lampfittings for general illumination and panel lighting by a special row of lampfittings following the contours of the instrument panels.
To provide sufficient vertical illuminance on the panels this special row will consist of lampfittings with prismatic lenses causing an asymmetric lighting.
Distribution or of lampfittings mounted in a sloping position and very accurately located to minimize reflections from the meter faces.
If required fluorescent lampfittings installed in control rooms containing electronic instrumentation shall be provided with means to reduce radio interference.
To avoid stroboscopic effect (cyclic flicker) following measurements shall be taken:
- single pin, instant start type tubes shall be inserted in two way lampfittings such that their starting strips are anti parallel.
- in multi way lampfittings each tube shall be connected to a separate phase.
- in single phase circuits duo compensated lampfittings shall be used.
Supply system voltage shall possibly be the same as selected for the low voltage power distribution system, supposing that it has a solidy earthed neutral.
5.2If the above is not feasible separate lighting transformers fed from the low voltage power distribution system shall be applied. Dependant on the lighting load expected these transformers shall be single or three phase with respectively one phase or the neutral (fully sized) of the secondary winding solidly earthed.
5.3Maximum voltage drop at the terminals of the lampfittings shall not exceed 3%; e.g. 1% in the feeder system of the lighting panels and 2% in the branch-circuits.
Lighting panels shall be located in compliance with the requirements for economic installation and admissible voltage drop in the circuits.
Each lighting panel shall have a main switch.
Circuits may be either 3 phase, 4 wire or single phase 2 wire.
Special attention should be given to balancing the connected loads on these circuits between the 3 phases to the maximum extent practical.
Maximum rating of lighting panel circuits shall be 16 amps unless a higher rating is required for discrimination purposes. (e.g. when circuit breakers are used in lighting poles).
One spare circuit shall be provided for each five initial circuits used.
Connected load of each circuit shall not exceed 80 percent of the circuit rating.
Circuits serving road-, plant- and area lighting shall be fed from a contactor and controlled by means of a photocell with manual overriding facilities.
Separate circuits shall be used for grade lighting and lighting for platforms or other above grade structures.
Convenience outlets, gauge glasses and indoor lighting shall be supplied by continuously energized circuits.
Lighting of indoor areas and when required gauge glass assemblies, shall have local switches.
Circuits supplying convenience outlets shall be provided with 30 mA earth leakage protection.
The arrangement of circuits in an area or unit shall be such that sufficient orientation lighting will remain when one circuit or one phase of a threephase circuit should be disrupted.
7. Convenience Outlets and Handlamps
Convenience outlets shall be installed in process and utility areas such that every location can be reached with an extension cord of 20 meters.
Convenience outlets shall be two wire, 3 pole, 16 amps.
The third pole shall be solidly connected to earth.
Voltage shall preferably be the same as selected for the lighting installation.
Handlamps and small tools shall be supplied through portable single phase safety transformers, which will be provided with a flexible cable and plug for connection to the convenience outlets.
In the event of a power failure, enough illumination should be kept in service by emergency supply devices to enable operating personnel to follow their emergency operating and/or shutdown procedures and/or to leave certain buildings or areas.
Areas where emergency illumination is necessary are control rooms, electrical substations, strategic points in the process areas, laboratories, exit stairs and passageways, fire fighting stations, medical rooms, air craft warning light, plant entrances and perimeter air craft warning light, plant entrances and perimeter lighting. (when the perimeter lighting is for plant security).
The emergency lighting shall be combined with the normal lighting when calculating the illuminance level.
The emergency lighting system shall be supplied from the normal lighting supply and be switched automatically to an alternative source of supply upon loss of A.C. power.
If provided, the alternative source of supply for the power system (e.g. a standby generator) shall also be used for the emergency lighting system.
In addition, or when alternative sources of supply for the power system are not provided, self contained rechargeable battery units sufficient for 2 hours operation without AC power shall be installed. These units shall be either individual or common for a group of lampfittings and will switch automatically to battery source upon loss of A.C. power, provided that lampfittings have been switched on.
Mercury vapour lamps and similar types shall not be used for emergency lighting due to the length of the restrike time (3 to 7 minutes) after a disruption of supply.
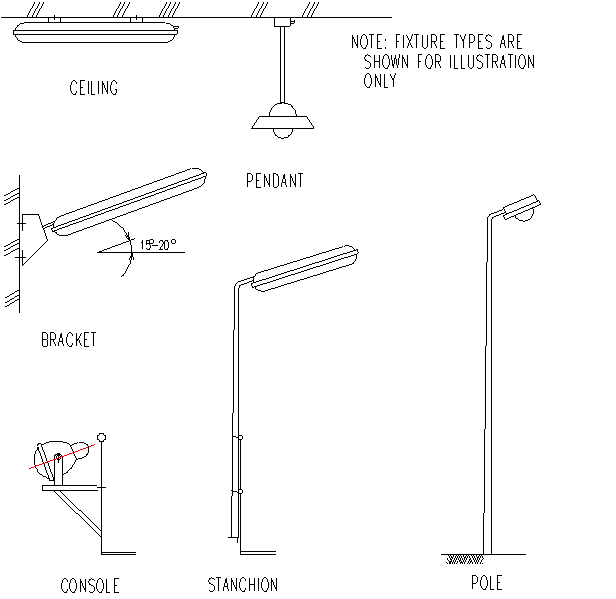
9. Coding System of Lampfittings
Lampfittings are indicated on drawings with a coding system as follows:
LP2 - 3 - A - R - a
Explanation:
LP2 = Lighting panel No. (When confusion is not likely, this identification can be given by a note on the drawing concerned)
3 = Circuit No.
A = Fixture reference (see item 9.2.)
R (S-T) = Phase identification (only in case of 3 phase circuits)
a (b,c etc) = Reference to local switch (only when required)
Fixture reference shall be made per job on the coversheet for lighting panel schedules or typical detail drawing for lighting.
The reference shall include: Design of enclosure, lamp, type and mounting.
Example:
|
Reference |
Enclosure |
Lamp |
Type |
Mounting |
|
A B C F G K |
Restr. Ex. pr Restr. Ex. pr Restr. Ex. pr Restr. Ex. pr Normal Normal |
Fluorescent 2x40W Fluorescent 2x40W Fluorescent 2x20W Fluorescent 2x40W Merc. vapour 250W Merc. vapour 2x85W |
gen. purpose gen. purpose slip over slip over floodlight streetlight |
see fig. 9.1 |
Type of Mounting figure 9.1
The data given cover the minimum average lighting requirements in lux at an elevation as indicated.
|
Initial |
in Service |
at Elevation |
Remarks |
|||
|
1. |
Process areas Pump rows, valves and manifolds Heat exchangers Operating platforms Ordinary platforms/walkways Ladders Stairs Equipment areas Working floors Compressor houses Analyzer houses Boilers operating front Boilers Panel Boilers Panel Open yards (between proces units) Control room: Panel Console Back of panel General area Emergency Computer rooms |
70 70 70 30 30 70 70 70 200 500 70 225 200 7 400 400 100 450 45 500 |
50 50 50 20 20 50 50 50 150 350 50 150 150 5 300 300 70 300 30 350
|
Ground Ground Floor Floor Landings Floor Ground Floor Floor Floor Floor Ground Vertical Ground Vertical Hor/Vert. 75 cm 75 cm 75 cm Ground |
If required Asymmetric Asymmetric |
|
|
2. |
Non process areas Pump area for loading/unloading Loading racks: general loading point Tanker docks: general Hose handling Manifold Loading Tankfields: Stairs Manifolds Roads Street/Roads: Heavy traffic Light traffic Fence protective lighting Parking lots Substations: General Operating aisles Emergency Transf. yards Basement Outdoor switchracks
|
70 70 200 30 150 150 200 15 15 3 7 5 3 2
150 200 30 30 20 70 |
50 50 150 20 100 100 150 10 10 2 5 3 2 1
100 150 20 20 15 50
|
Ground Floor Point Floor Floor Floor Point Stair Ground Ground Ground Ground Ground Ground
Floor Floor Floor Ground Floor 100 cm |
If required
|
|
|
3. |
Buildings Offices general Drafting offices Reception Conference rooms Toilets Lockerrooms change-houses First aid room Stairways, corridors, etc. Laboratories Canteens: general kitchen Entrance gate-house + clocking Entrance gate (inspection) Warehouse: indoors yard Workshops: general medium Benches + Machines Garages: general Repair |
750 1200 150 400 70 150 700 150 700 150 300 150 225 75 7 300
700 150 450 |
500 800 100 300 50 100 500 100 500 100 200 100 150 50 5 200
500 100 300
|
75 cm 75 cm 75 cm 75 cm 75 cm 75 cm 75 cm Floor 100 cm 75 cm 75 cm Floor Floor Floor Ground Floor
75 cm Floor Floor |
Spot lighting
Pits only |
|

