Table of Contents
- Purpose
- General
- Definitions
- Responsibilities
- Procurement
- Acceptance - Check
- Storage
- Redrying
- Issue
- Document Control
- Training Center
- References
- Attachments
1. Purpose
This document establishes the guidelines for purchasing, acceptance, storage, drying and issue of welding materials at construction sites for larger projects and has to be amended for small projects.
The welding materials will be stored at and issued by the subcon tractor's welding material control center and issue center(s).
2. General
Where subcontract companies are engaged in welding operations on the construction site, the control and storage system they propose to use will require approval by the Company Site Quality Assurance Manager in the operations center from which the subcontract was raised, but in any case shall follow substantially the details contained in this procedure.
The subcontractor's welding material control system is to be de signed so as to ensure that at construction sites welding materials will be issued of the specified quality and in a good condition to assist in producing welds of the specified condition.
3. Definitions
| Welding Rods |
|
| Welding Consumables |
|
| Welding Materials |
|
| Welding Material Control Center |
|
| Welding Material Issue Station |
|
| Low Hydrogen Electrodes |
|
| American terminology(ANSI/AWS A3.0.80) |
|
| GTAW: | TIG: |
|
|
| GMAW: | MAG respectively MIG: |
|
|
| SAW: | |
|
|
| SMAW: | |
|
|
| FCAW: | |
|
|
4. Responsibilities
The Subcontractor is responsible for welding material control center and issue stations. He shall:
- Establish and manage the organization and requirements necessary to receive,store, dry where required and issue welding materials.
- Establish the necessary welding material issue stations as required.
- Provide the necessary personnel to man these areas.
- Accept and check welding consumables and shielding gases as they arrive at the welding material control center.
- Store welding consumables and shielding gases.
- Dry and bake covered electrodes in accordance with manufacturers' recommendations.
- Ensure that all welding consumables hold a current certificate from an independent Inspection Authority, indicating that the electrodes (or electrode-flux combination) will meet the requirements of the classification or grade.
The Company Site QA Manager is responsible for:
- Ensuring that the subcontractor establishes a system of controlling welding materials at the job site, which covers the aspects of this guide.
5. Procurement
Purchase requisitions for welding consumables shall be initiated by the appropriate Welding Engineer of the subcontractor. Requisitions shall specify, where applicable:
- Applicable classification of SMAW covered electrode, GTAW filler rod, and filler wire for GMAW, FCAW and SAW
- Applicable classification of SAW flux
- Applicable classification and type of shielding gas, after verification of the purity of shielding gas
- Size and quantity of specific items
- Special marking or identification requirements
- Packing
- Special requirements on chemical composition, mechanical properties and approval by IIA.
6. Acceptance - Check
The responsibility for the acceptance check of welding consumables and shielding gases, shall be in accordance with the procedure below.
The subcontractor's welding material control center personnel shall identify welding consumables for conformity to requisition/purchase order, check on damage to packing and stamp the date of receipt on the packing.
On completion of checking, if all items are found to conform to the requisition/purchase order, the checker will verify this by endorsing the applicable document. Any items that do not conform, shall be segregated as discrepancy materials and the checker will initiate the "nonconformance" procedure (ref. 12.1).
7. Storage
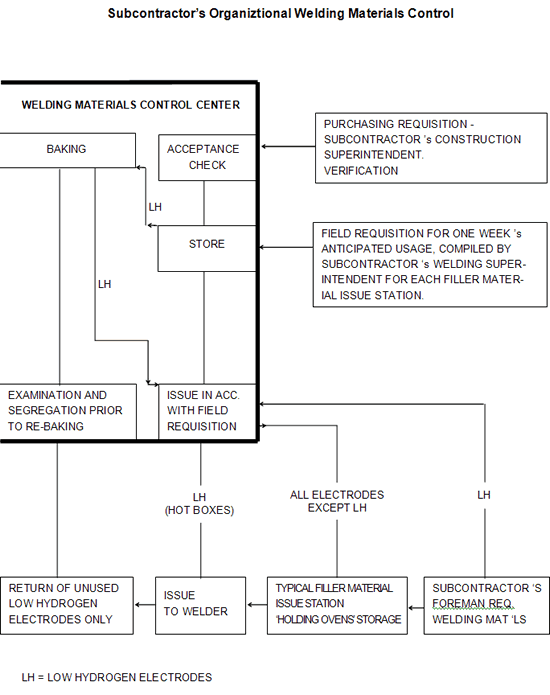
The duties relating to the storage of welding materials and shield ing gases shall be as follows (see also Attachment 2):
7.1 Welding Materials
All welding materials that can be damaged by moisture (electrodes, wires and fluxes) shall be kept in a dry, well ventilated store. For this purpose storage cabinets or rooms shall be established in the welding material control and issue center(s). The temperature in the cabinets and rooms shall be maintained at least 10°C above ambient in order to keep the relative humidity below 60%.
For the distribution of welding materials to the various areas of consumption on the construction site, a (number of) welding material issue station(s) shall be set up. These will be equipped with holding ovens operating at a temperature of between 130°C and 150°C for storage of low hydrogen electrodes (see Attachment 2).
In the welding material control and issue center(s), unopened containers shall be warehoused in the storage room clear of direct contact with the ground and stacking of containers shall be such as to avoid damage to the contents.
GTAW filler rod, and GMAW, FCAW and SAW filler wire shall be stored under the same conditions as for covered electrodes and shall be kept in their protective wrappers until ready for use.
7.2 Shielding Gases
Full cylinders of gases shall be stored upright and firmly fixed to prevent damage.
All cylinders will be stored in locked cylinder sheds. This building will be divided into sections to separate the types of gases. Empty cylinders will be stored separately.
The Company Site QA Manager is entitled to check storage methods and conditions at any time, and to advise where the need arises.
8. Redrying
The drying/baking of covered electrodes, shall also be in accordance with the details in Attachment 1.
If Attachment 1 is in contradiction with the manufacturers instruc tions, the Welding Superintendent shall decide.
9. Issue
9.1 The issue of welding materials shall be carried out in a controlled manner and in accordance with the following procedure:
Responsible personnel shall be designated by the subcontractor's Welding Superintendent for the operation and maintenance of the storage and issue areas.
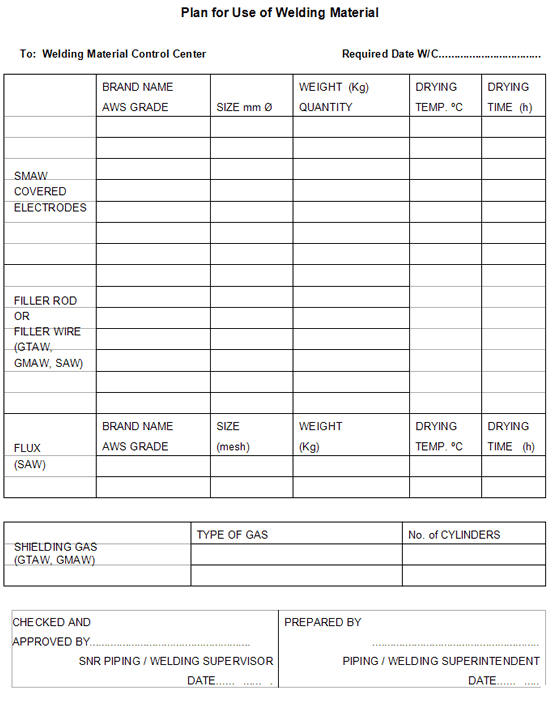
Consumption requirements for welding materials shall be determined by the appropriate subcontractor's Welding Engineer, who will advise the welding material control center of his weekly expected consump tion by compiling "plan for use of welding material" (Attachment 2). This document will nominate brand names, AWS grade, sizes, quantities, weights and any special drying conditions. It is intended that the information contained in this document will enable the welding material control center to issue to the applicable filler material issue station all welding consumables for the next week's usage.
Before issuing, the welding electrodes shall be checked on the moisture content of the cover. If necessary the electrodes shall be redried (see Attachment 1).
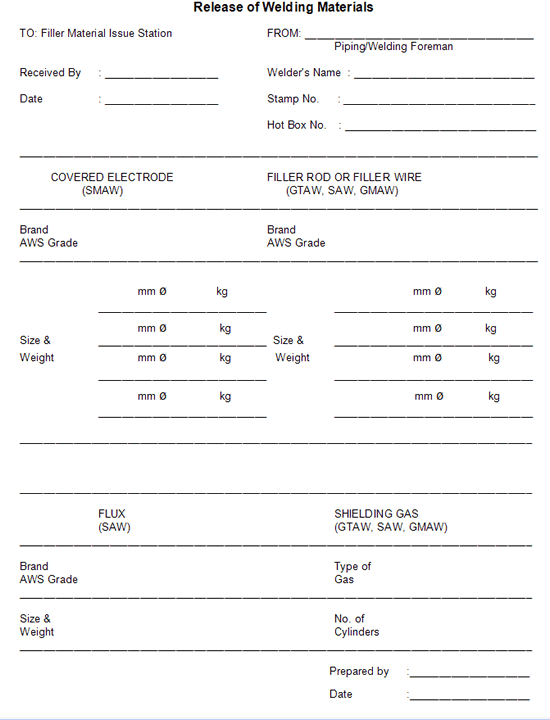
The form "release of welding material" (Attachment 3) will be compiled by the subcontractor's Welding Foreman for each welder or welding operator as required. The form will nominate the brand name, AWS grade, size and quantity of welding materials required and will be authorized for issue.
Where low alloy/low hydrogen electrodes are requested, they shall be issued in welders' "hot boxes", which will be identified with a discrete number and the appropriate electrode type to avoid mixing. The date and time of issue of each "hot box" containing low alloy/ low hydrogen electrodes shall be logged at the time of issue (Attachment 4).
Low hydrogen electrodes unused at the end of the work shift shall be returned to the welding material control center, where they shall be segregated for baking and reissue. Electrodes shall only be redried a maximum of 2x. Any partly used or damaged electrodes of this type shall be discarded.
9.2 When using any low, hydrogen-covered electrodes, welders must ensure that they are used direct from "hot boxes" maintaining a temperature of between 70°C and 100°C. The lids of "hot boxes" shall be kept closed, except when withdrawing electrodes. There shall only be one type electrode in the "hot box" at any one time to avoid mixture or misuse.
Cellulose and Rutile type electrodes will be issued to welders in limited quantities, i.e. not more that 2 kg direct from the storage area. These shall be kept in and used from the "quiver" provided to each welder as standard equipment.
GTAW, SAW and GMAW filler wire and rod will be issued as required direct from the dry storage are (see paragraph 7.1).
SAW flux will be issued on a daily basis as required direct from moisture resistant bulk containers (either drum or bagged) and all unused or contaminated flux shall be returned to the issue point for reconditioning to the manufacturers' recommendations or otherwise discarded.
Shielding gases shall be issued by the use of the "release of welding material" form compiled by the Welding Foreman.
The Company Site QA Manager shall check the issue system of welding materials and advise where necessary.
10. Document Control
Attachment 5 shows the procedure of preparation and recording of relevant documents.
11. Training Center
The special nature of a welder training center will entail the set-up of an independent storage and issue area, but it will, in general, follow substantially the details contained in this proce dure.
12. References
| Document Number | Title | Level | |
| 12.1 | CO-QC-10 | Handling of Non-conformities | 3 |
| 12.2 | CO-QC-16 | Inspection Procedure for Field Welding | 3 |
13. Attachments
- Redrying and Storage Conditions for SMAW Covered Electrodes and Fluxes
- Plan for Use of Welding Material
- Release of Welding Materials
- Low Hydrogen Electrodes -- Issue Log
- Document Flow for Welding Materials Issue and Control
- Subcontractor's Organizational Welding Material Control
1. Redrying and Storage Conditions for SMAW Covered Electrodes and Fluxes
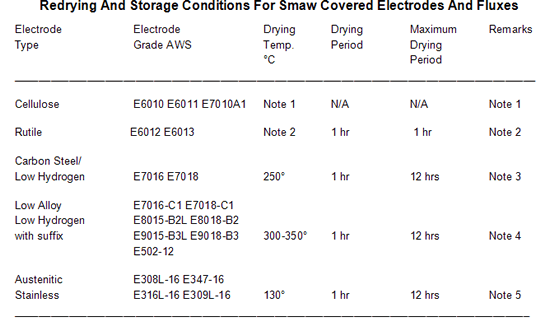
Note 1: Cellulose electrodes shall be stored dry and are not to be heated.
Note 2: Rutile electrodes shall be stored dry and if they have become damp shall be dried for one hour at 120°C before use.
Note 3: Carbon steel/low hydrogen electrodes do not require baking unless affected by moisture, in which case they will be treated as for low alloy/low hydrogen, i.e. 300-350°C. These electrodes shall be used from welders' hot boxes.
Note 4: Low hydrogen-covered electrodes with a suffix are subject to special require ments for storage, baking and issue.
Note 5: These electrodes do not require baking unless affected by moisture, in which case they are baked for one hour at 150°C prior to use.
2. Plan for Use of Welding Material
3. Release of Welding Materials
4. Low Hydrogen Electrodes -- Issue Log

5. Document Flow for Welding Materials Issue and Control

6. Subcontractor's Organizational Welding Material Control